
SSH can use either "RSA" (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) or "DSA" ("Digital Signature Algorithm") keys. Other authentication methods are only used in very specific situations.
#Linux ssh keygen root password
Key-based authentication has several advantages over password authentication, for example the key values are significantly more difficult to brute-force, or guess than plain passwords, provided an ample key length.

Key-based authentication is the most secure of several modes of authentication usable with OpenSSH, such as plain password and Kerberos tickets. Different SSH programs generate public keys in different ways, but they all generate public keys in a similar format: In fact, if you don't mind leaving a private key unprotected on your hard disk, you can even use keys to do secure automatic log-ins - as part of a network backup, for example. Public key authentication is a much better solution than passwords for most people. Wikipedia has a more detailed explanation of how keys work. As an extra security measure, most SSH programs store the private key in a passphrase-protected format, so that if your computer is stolen or broken in to, you should have enough time to disable your old public key before they break the passphrase and start using your key. When you log in to a computer, the SSH server uses the public key to "lock" messages in a way that can only be "unlocked" by your private key - this means that even the most resourceful attacker can't snoop on, or interfere with, your session. ssh/authorized_keys file on all the computers you want to log in to. The private key is kept on the computer you log in from, while the public key is stored on the. Each key is a large number with special mathematical properties. With public key authentication, the authenticating entity has a public key and a private key.
#Linux ssh keygen root Pc
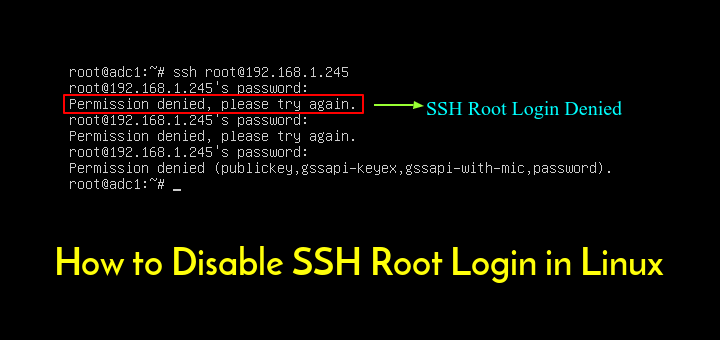
My computer - a perfectly ordinary desktop PC - had over 4,000 attempts to guess my password and almost 2,500 break-in attempts in the last week alone. If you don't think it's important, try logging the login attempts you get for the next week. This is particularly important if the computer is visible on the internet. Public key authentication is more secure than password authentication. Learn more SSH commands in this tutorial.Parent page: Internet and Networking > SSH Now you can to configure and connect to a remote system using SSH key pairs. The system now no longer allows password authentication for logins. Restart the SSH service by entering the following: sudo systemctl restart ssh Find and modify the following lines to look as follows: PasswordAuthentication noĤ. Next, edit the sshd_config file in a text editor of your choice (we are using nano): sudo nano /etc/ssh/sshd_configģ. This username should have sudo privileges.Ģ. Start by logging into the remote server: ssh You are logging into the server with a sudo user account.ġ.You can log into the server without a password (such as using an SSH connection with a key pair, detailed in this article).It prevents brute-force attacks against attempting to log in to the server.īefore continuing, double-check to make sure: Step 5: Disable Password Authentication (Optional)ĭisabling password authentication is a security precaution. You should now have an SSH connection to the remote server. If you set a passphrase during Step 2, enter it when prompted. The system may display that the authenticity of the host can’t be established. From the client system, open a terminal window and enter the following: ssh Ģ.


If you’re using the root Debian user account on the server, the directory owner must be set to the user account that will be logging in remotely to the server: sudo chown -R user:user ~/.ssh Step 4: Log in Remotely Using SSHġ. Set the correct permissions for the new directory: sudo chmod -R go= ~/.sshħ. Replace ssh_public_key with the actual public key displayed by the cat command.Ħ. Next, add the public key to the authorized_keys file by entering the following: sudo echo ssh_public_key > ~/.ssh/authorized_keys Note: If the ~/.ssh directory already exists, the command will exit without making changes.ĥ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
